All categories
Gouty Arthritis
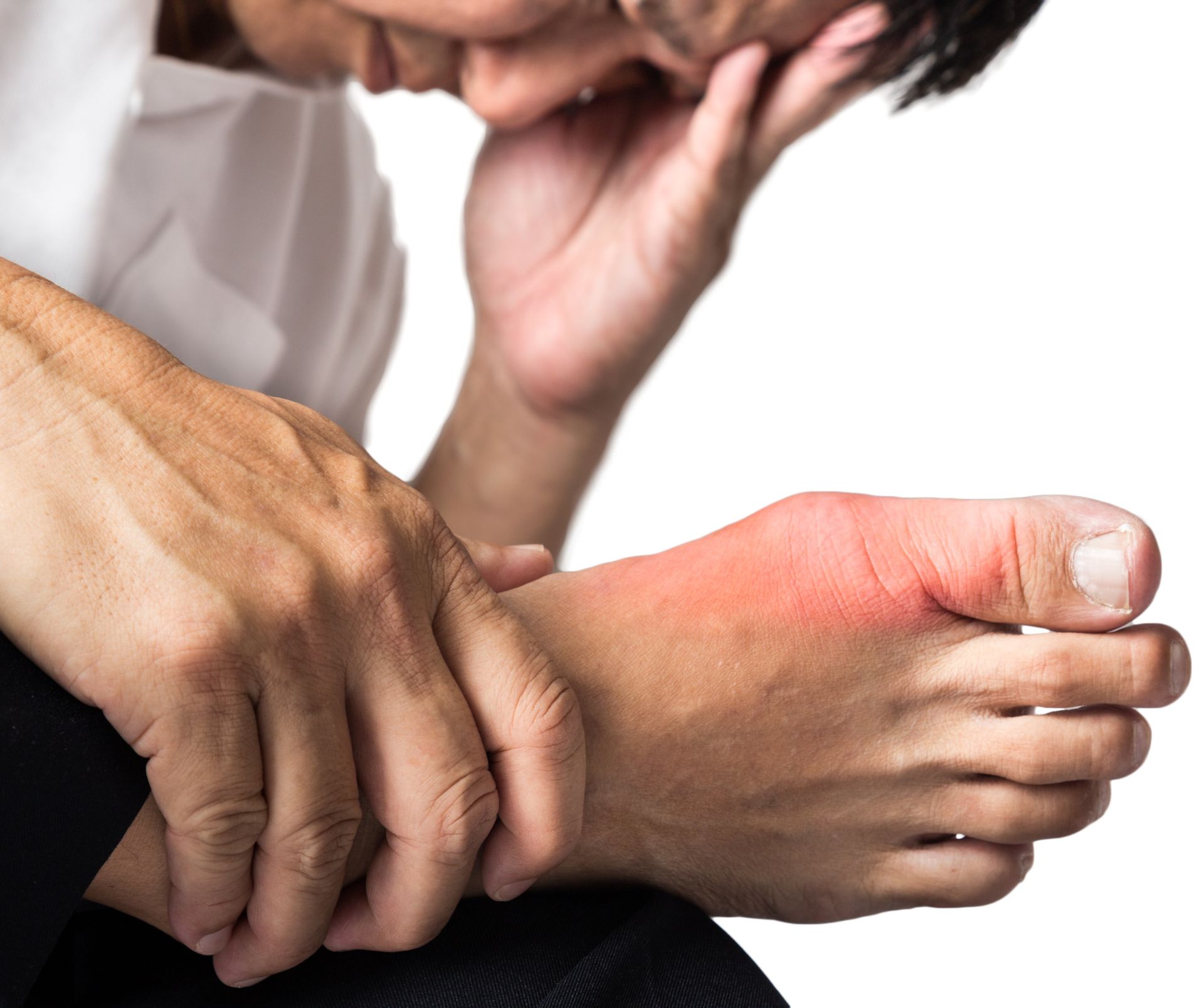
Gout (gouty arthritis) is a metabolic pathology of the body in which the metabolism of purines (uric acid derivatives) is affected, which leads to excessive deposition of uric acid salts in some tissues of the body. Exactly, as a result of these deposits, dysfunctions of organs and tissues are formed. The joints, kidneys and some other organs (bones, ligaments, liver) are especially affected. The basis of gout is a genetically inherited defect in the metabolic processes of uric acid, a defect in enzymes that help its utilization and excretion, as well as defects in the system of internal synthesis of purine substances. Gout attacks can be triggered by stress reactions to alcohol, citrus fruits, viral infections, physical or mental stress, trauma and hypothermia, bruises, pressure fluctuations and medication.

